PostgreSQL完成按月累加的操作
背景
统计某个指标,指标按照月进行累加,注意需要按省份和年份进行分组。
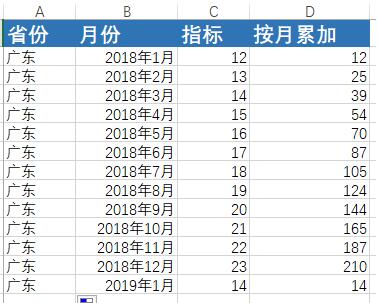
方法一、使用自关联
-- with 按月统计得到中间结果 WITH yms AS (SELECT regionid,SUM(getnum) AS getnum,SUM(dealnum) AS dealnum,to_char(qndate,'yyyy-MM') AS yearmonth FROM t_queuenumber GROUP BY regionid,to_char(qndate,'yyyy-MM') ORDER BY regionid,yearmonth)-- 查用子查询解决。 SELECT s1.regionid,s1.yearmonth, getnum,dealnum, (SELECT SUM(getnum) FROM yms s2 WHERE s2.regionid = s1.regionid AND s2.yearmonth <= s1.yearmonth AND SUBSTRING(s1.yearmonth,0,5) = SUBSTRING(s2.yearmonth,0,5) ) AS getaccumulatednum, (SELECT SUM(dealnum) FROM yms s2 WHERE s2.regionid = s1.regionid AND s2.yearmonth <= s1.yearmonth AND SUBSTRING(s1.yearmonth,0,5) = SUBSTRING(s2.yearmonth,0,5) ) AS accumulatednum FROM yms s1;
查询的结果如下:
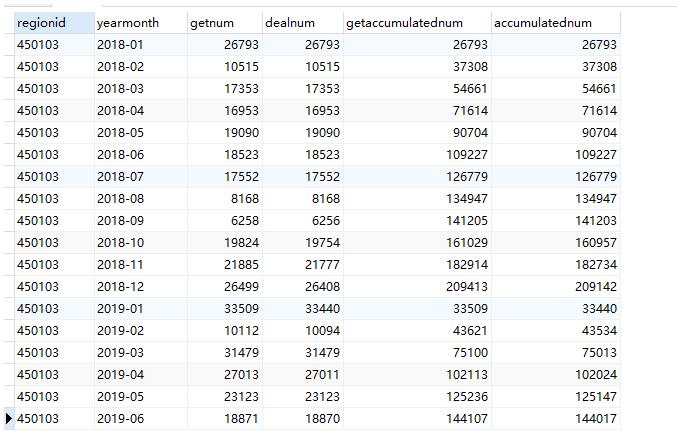
方法二、使用窗口函数
更多关于窗口函数的用法,可以参考以前的文章。窗口函数十分适合这样的场景:
WITH yms AS (SELECT regionid,SUM(getnum) AS getnum,SUM(dealnum) AS dealnum,to_char(qndate,'yyyy-MM') AS yearmonth FROM t_queuenumber GROUP BY regionid,to_char(qndate,'yyyy-MM') ORDER BY regionid,yearmonth) -- 窗口函数的使用 SELECT regionid,yearmonth, SUM(getnum) OVER(PARTITION BY regionid,SUBSTRING(yearmonth,0,5) ORDER BY yearmonth) AS getaccumulatednum, SUM(dealnum) OVER(PARTITION BY regionid ,SUBSTRING(yearmonth,0,5) ORDER BY yearmonth) AS dealaccumulatednum FROM yms;
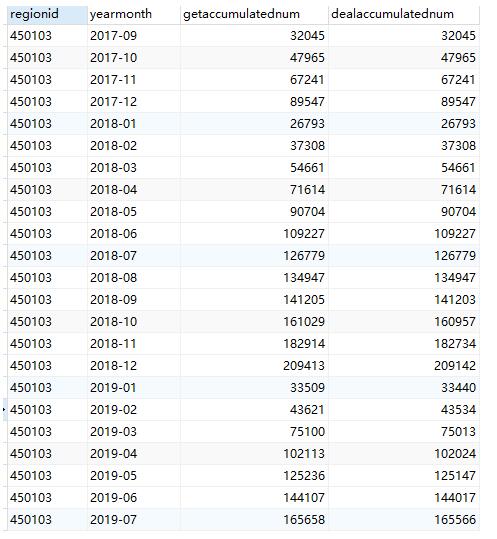
后记
可以使用子查询、可以使用窗口函数完成上面业务场景。
补充:PostgreSQL实现按秒按分按时按日按周按月按年统计数据
提取时间(年月日时分秒):
import datetime
from dateutil.relativedelta import relativedelta
today = str(datetime.datetime.now())
print(today)
print(today[:4], today[:7], today[:10],today[:13])
print("************分隔符***************")
yesterday = (datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=-1)).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
yesterday2 = (datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=-2)).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
nextmonths = str(datetime.date.today() - relativedelta(months=-1))[:7]
lastmonths = str(datetime.date.today() - relativedelta(months=+1))[:7]
lastyears = str(datetime.date.today() - relativedelta(years=+1))[:4]
nextyears = str(datetime.date.today() - relativedelta(years=-1))[:4]
print(yesterday)
print(yesterday2)
print(nextmonths)
print(lastmonths)
print(lastyears)
print(nextyears)
结果:
2020-03-05 13:49:59.982555 2020 2020-03 2020-03-05 2020-03-05 13 ************分隔符*************** 2020-03-04 13:49:59 2020-03-03 13:49:59 2020-04 2020-02 2019 2021
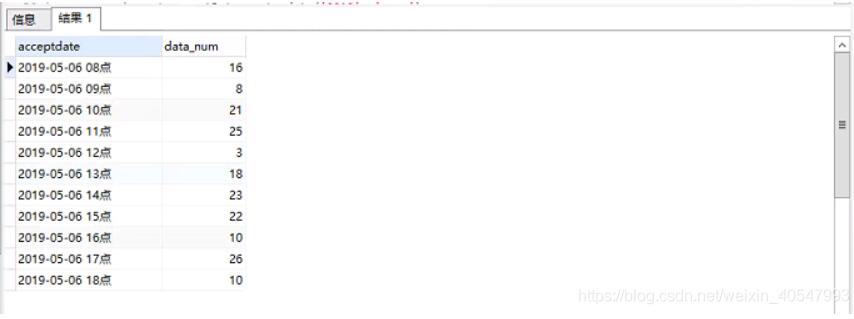
昨日每时:
select s.acceptDate, s.data_num
from (select to_char(acceptDate, 'yyyy-mm-dd hh24') || '点' as acceptDate,
count(1) as data_num
from table_name t
where t.acceptDate >= to_date('20190506', 'yyyymmdd')
and t.acceptDate < to_date('20190507', 'yyyymmdd') and organization_ = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
group by to_char(acceptDate, 'yyyy-mm-dd hh24') || '点') s
本月每天:
select s.acceptDate, s.data_num
from (select to_char(acceptDate, 'yyyy-mm-dd') as acceptDate,
count(1) as data_num
from table_name t
where t.acceptDate >= to_date('201905', 'yyyymm')
and t.acceptDate < to_date('201906', 'yyyymm') and organization_ = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
group by to_char(acceptDate, 'yyyy-mm-dd') ) s
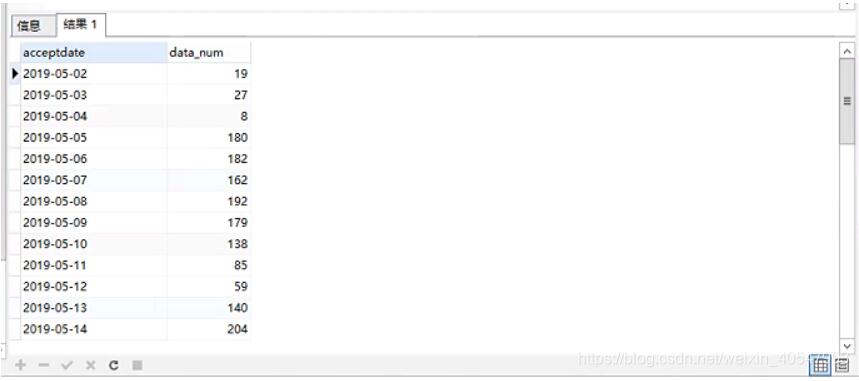
本年每月:
select s.acceptDate, s.data_num
from (select to_char(acceptDate, 'yyyy-mm') as acceptDate,
count(1) as data_num
from table_name t
where t.acceptDate >= to_date('2019', 'yyyy')
and t.acceptDate < to_date('2020', 'yyyy') and organization_ = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
group by to_char(acceptDate, 'yyyy-mm') ) s

2月-7月中每月的人数统计:
sql = """SELECT to_char(rujiaoriqi, 'yyyy-mm') as month,count(1) num
FROM jibenxx where rujiaoriqi is not null and zhongzhiriqi is null
AND to_char(rujiaoriqi,'yyyy-mm-dd')>='2020-02-01'
GROUP BY to_char(rujiaoriqi, 'yyyy-mm') order by to_char(rujiaoriqi, 'yyyy-mm') """
统计每年:
select s.acceptDate, s.data_num
from (select to_char(acceptDate, 'yyyy') as acceptDate,
count(1) as data_num
from table_name t
where t.acceptDate >= to_date('2015', 'yyyy')
and t.acceptDate < to_date('2021', 'yyyy') and organization_ = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
group by to_char(acceptDate, 'yyyy') ) s

里面时间参数进行传参即可。
补充:
统计今天(查询当天或者指定某天数量)
select count(1) FROM "shequjz_jibenxx" where to_char(zhongzhiriqi,'yyyy-mm-dd')='2019-11-11'
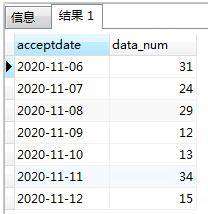
最近七天每天的数量:
select s.acceptDate, s.data_num
from (select to_char(jiaozheng_jieshushijian, 'yyyy-mm-dd') as acceptDate,
count(1) as data_num
from shequjz_jibenxx t
where t.jiaozheng_jieshushijian >= to_date('2020-11-06', 'yyyy-mm-dd')
and t.jiaozheng_jieshushijian < to_date('2020-11-13', 'yyyy-mm-dd')
group by to_char(jiaozheng_jieshushijian, 'yyyy-mm-dd') ) s ORDER BY acceptDate ASC
最近七天(1天、3天、7天、一个月、一年、1h、1min、60s)的数量(总量):
# 包括今天向前推6天的总量 select count(1) from shequjz_jibenxx where jiaozheng_jieshushijian between (SELECT current_timestamp - interval '7 day') and current_timestamp # 最近一天(昨天) SELECT current_timestamp - interval '1 day' # 最近三天 SELECT current_timestamp - interval '3 day' # 最近一周 SELECT current_timestamp - interval '7 day' # 最近一个月(当前时间向前推进一个月) SELECT current_timestamp - interval '1 month' # 最近一年(当前时间向前推进一年) SELECT current_timestamp - interval '1 year' # 最近一小时(当前时间向前推一小时) SELECT current_timestamp - interval '1 hour' # 最近一分钟(当前时间向前推一分钟) SELECT current_timestamp - interval '1 min' # 最近60秒(当前时间向前推60秒) SELECT current_timestamp - interval '60 second'
最近七天中每天的累计历史总量:
步骤:
1)先统计出近7天每天的数量
2)后统计出7天前的累计历史总量
3)再对第(1)步中获取的结果进行累计求和,使用cumsum()函数
4)最后在第(3)步结果的基础上,加上7天前的累计历史总量(也就是第2步的结果)
# 趋势
def getWeekTrends(self):
try:
database = DataBase()
sql = """select s.zhongzhi_Date, s.data_num
from (select to_char(jiaozheng_jieshushijian, 'yyyy-mm-dd') as zhongzhi_Date,
count(1) as data_num
from shequjz_jibenxx t
where t.jiaozheng_jieshushijian >= to_date('{}', 'yyyy-mm-dd')
and t.jiaozheng_jieshushijian < to_date('{}', 'yyyy-mm-dd')
group by to_char(jiaozheng_jieshushijian, 'yyyy-mm-dd') ) s""".format(lastweek, today[:10])
res_df = database.queryData(sql, flag=True)
sql_total = """select count(1) FROM "shequjz_jibenxx" where rujiaoriqi is not null
and zhongzhiriqi is null and to_char(rujiaoriqi,'yyyy-mm-dd')<'{}'""".format(lastweek)
res_total = database.queryData(sql_total, count=1, flag=False) #7131
res_df['cumsum'] = res_df['data_num'].cumsum() # 累计求和
res_df['cumsum'] = res_df['cumsum'] + res_total[0]
res_df = res_df[['zhongzhi_date', 'cumsum']].to_dict(orient='records')
res = {'code': 1, 'message': '数据获取成功', 'data': res_df}
print(res)
return res
except Exception as e:
error_info = '数据获取错误:{}'.format(e)
logger.error(error_info)
res = {'code': 0, 'message': error_info}
return res
{'code': 1, 'message': '数据获取成功', 'data': [
{'zhongzhi_date': '2020-11-13', 'cumsum': 7148},
{'zhongzhi_date': '2020-11-10', 'cumsum': 7161},
{'zhongzhi_date': '2020-11-11', 'cumsum': 7195},
{'zhongzhi_date': '2020-11-12', 'cumsum': 7210},
{'zhongzhi_date': '2020-11-09', 'cumsum': 7222},
{'zhongzhi_date': '2020-11-14', 'cumsum': 7229},
{'zhongzhi_date': '2020-11-15', 'cumsum': 7238}]}
postgresql按周统计数据
(实际统计的是 上周日到周六 7天的数据):
因为外国人的习惯是一周从周日开始,二我们中国人的习惯一周的开始是星期一,这里 -1 即将显示日期从周日变成了周一,但是内部统计的数量还是从 上周日到周六进行 统计的,改变的仅仅是显示星期一的时间。
提取当前星期几: 1
SELECT EXTRACT(DOW FROM CURRENT_DATE)
提取当前日期: 2020-11-16 00:00:00
SELECT CURRENT_DATE-(EXTRACT(DOW FROM CURRENT_DATE)-1||'day')::interval diffday;
按周统计数据一:
select to_char(jiaozheng_jieshushijian::DATE-(extract(dow from "jiaozheng_jieshushijian"::TIMESTAMP)-1||'day')::interval, 'YYYY-mm-dd') date_, count(1) from shequjz_jibenxx where jiaozheng_jieshushijian BETWEEN '2020-01-01' and '2020-11-16' GROUP BY date_ order by date_
其中date_为一周中的第一天即星期一
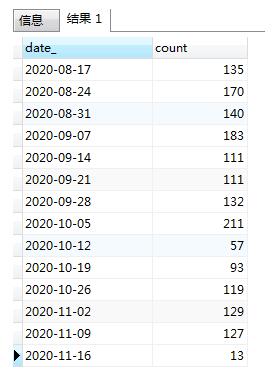
按周统计数据二:
SELECT to_char ( cda.jiaozheng_jieshushijian, 'yyyy ' ) || EXTRACT ( WEEK FROM cda.jiaozheng_jieshushijian ) :: INTEGER AS date_, count( cda.id ) AS count, cda.jiaozheng_jieshushijian AS times FROM shequjz_jibenxx AS cda WHERE 1 = 1 AND to_char ( cda.jiaozheng_jieshushijian, 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS' ) BETWEEN '2020-10-01 00:00:00' AND '2020-11-12 00:00:00' GROUP BY date_, times ORDER BY date_, times DESC

postgresql中比较日期的四种方法
select * from user_info where create_date >= '2020-11-01' and create_date <= '2020-11-16'
select * from user_info where create_date between '2020-11-01' and '2020-11-16'
select * from user_info where create_date >= '2020-11-01'::timestamp and create_date < '2020-11-16'::timestamp
select * from user_info where create_date between to_date('2020-11-01','YYYY-MM-DD') and to_date('2020-11-16','YYYY-MM-DD')
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
赞 (0)

