spring中bean id相同引发故障的分析与解决
前言
最近因为同事bean配置的问题导致生产环境往错误的redis实例写入大量的数据,差点搞挂redis。经过快速的问题定位,发现是同事新增一个redis配置文件,并且配置的RedisSentinelConfiguration的id是一样的,然后在使用@Autowired注入bean的时候因为spring bean覆盖的机制导致读取的redis配置不是原来的。
总结起来,有两点问题:
- 为什么相同bean id的bean会被覆盖
- @Autowired注解不是按照byType的方式进行注入的吗
代码如下:
public class UserConfiguration {
private int id;
private String name;
private String city;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
}
UserClient:
public class UserClient {
private UserConfiguration configuration;
public UserClient(UserConfiguration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
public String getCity() {
return configuration.getCity();
}
}
beans.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userConfiguration" class="com.rhwayfun.springboot.starter.rest.UserConfiguration">
<property name="id" value="${user1.id}"/>
<property name="name" value="${user1.name}"/>
<property name="city" value="${user1.city}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="userClient" class="com.rhwayfun.springboot.starter.rest.UserClient" autowire="byName">
<constructor-arg ref="userConfiguration"/>
</bean>
</beans>
beans2.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userConfiguration" class="com.rhwayfun.springboot.starter.rest.UserConfiguration">
<property name="id" value="${user2.id}"/>
<property name="name" value="${user2.name}"/>
<property name="city" value="${user2.city}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="userClient2" class="com.rhwayfun.springboot.starter.rest.UserClient">
<constructor-arg ref="userConfiguration"/>
</bean>
</beans>
application.properties:
user1.id=1 user1.name=bean1 user1.city=Hangzhou user2.id=2 user2.name=bean2 user2.city=Shanghai
Applition:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application{
@Autowired
UserClient userClient2;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
String city = userClient2.getCity();
System.out.println(city);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
运行程序,你会发现不管注入的userClient2还是userClient1,输出的结果都是Shanghai。但是我们想实现的是,注入userClient1的时候输出的应该是Hangzhou,注入userClient2的时候输出的应该是Shanghai。这也是导致开头说的问题的源头所在。要实现这个效果很简单,UserConfiguration换一个名字就可以了。
但是,为什么换个名字就可以了呢,不同spring配置文件相同bean id的bean为什么不会分别创建呢?原因就在于spring 对具有相同bean id的实例做了覆盖处理。你可以理解为一个Map,key是bean id,value就是class,那么当两次put相同id的bean的时候自然就被覆盖了。
我们先回忆下bean的生命周期:
- 实例化
- 填充属性
- 调用BeanNameAware的setBeanName方法
- 调用BeanFactoryAware的setBeanFactory方法
- 调用ApplicationContextAware的setApplicationContext方法
- 调用BeanPostProcessor的预初始化方法
- 调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法
- 调用自定义的初始化方法
- 调用BeanPostProcessor的初始化方法
- 实例化完毕
问题出在注册bean定义的时候,我们可以控制台看到以下输出
Overriding bean definition for bean 'userConfiguration' with a different definition: replacing [Generic bean: class [com.rhwayfun.springboot.starter.rest.UserConfiguration]; scope=; abstract=false; lazyInit=false; autowireMode=0; dependencyCheck=0; autowireCandidate=true; primary=false; factoryBeanName=null; factoryMethodName=null; initMethodName=null; destroyMethodName=null; defined in file [/Users/chubin/IdeaProjects/spring-boot-learning-examples/ spring-boot-starter-rest/target/classes/beans.xml]] with [Generic bean: class [com.rhwayfun.springboot.starter.rest.UserConfiguration]; scope=; abstract=false; lazyInit=false; autowireMode=0; dependencyCheck=0; autowireCandidate=true; primary=false; factoryBeanName=null; factoryMethodName=null; initMethodName=null; destroyMethodName=null; defined in file [/Users/chubin/IdeaProjects/spring-boot-learning-examples /spring-boot-starter-rest/target/classes/beans2.xml]]
就是说beans.xml中配置的UserConfiguration被beans2.xml配置的UserConfiguration实例覆盖了。那么自然我们得到的结果是Shanghai了。
spring bean覆盖
经过上面的分析,我们已经知道是因为被覆盖的导致的,那么怎么体现的呢?遇到解决不了的问题,看源码往往能得到答案:
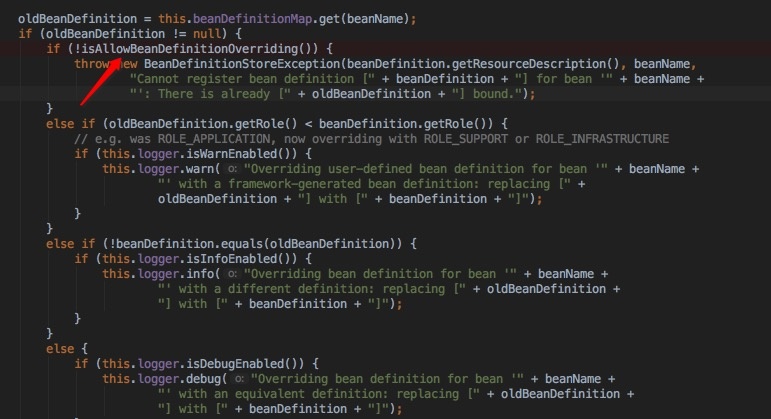
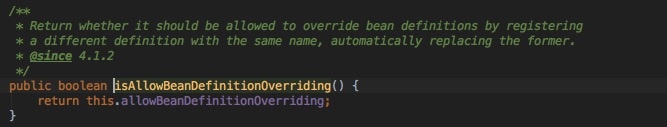
这段代码的逻辑就是,如果不允许具有相同bean id的实例存在就抛出异常,而这个值默认是true,也就是允许存在相同的bean id定义。
@Autowired注解实现机制
bean覆盖的问题解决了,那么还有一个问题,为什么使用@Autowired注入UserClient没有报错呢,明明配置了两个类型的bean啊。@Autowired不是按照byType注入的吗。
你确定吗?不完全正确。
因为@Autowired是spring提供的注解,我们可以看到是如何注入的代码,在AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredMethodElement.inject()方法中。
1.解析依赖
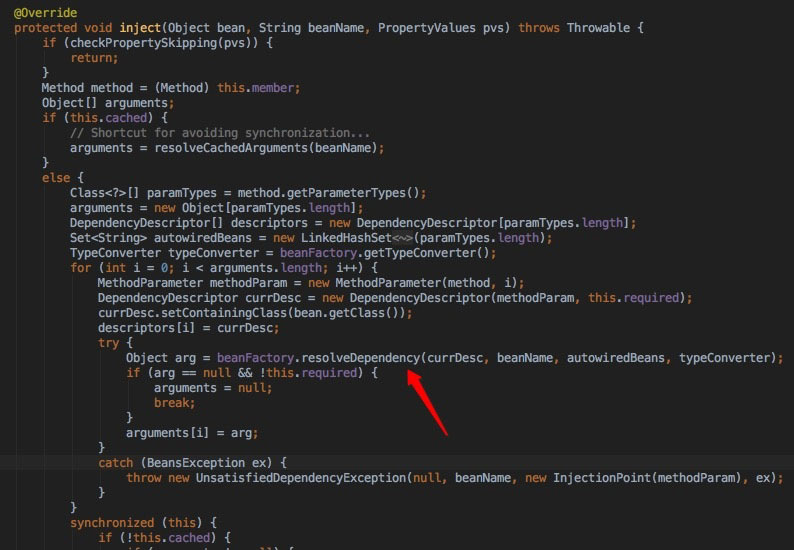
2.获取候选bean、决定最终被被注入的最优bean

3.最优bean的决策过程:1)判断时候有@Primary注解;2)如果没有,得到最高优先级的bean,也就是是否有实现了org.springframework.core.Ordered接口的bean(优先级比较,可以通过注解@Order(0)指定,数字越小,优先级越高);3)如果仍然没有,则根据属性名装配
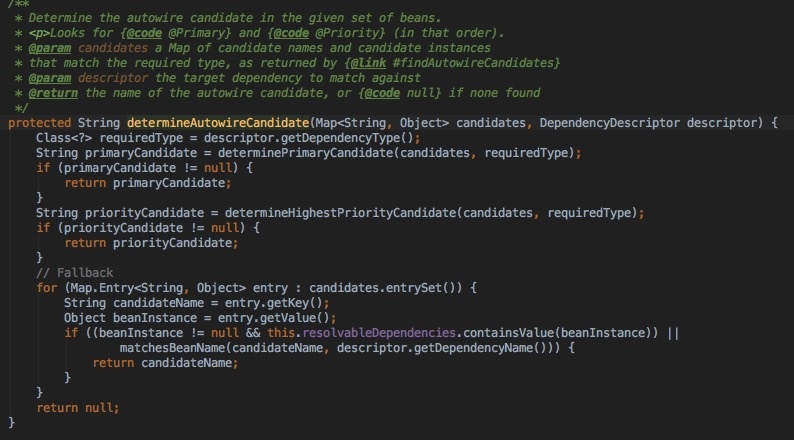
优先级定义:
/** * Useful constant for the highest precedence value. * @see java.lang.Integer#MIN_VALUE */ int HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE = Integer.MIN_VALUE; /** * Useful constant for the lowest precedence value. * @see java.lang.Integer#MAX_VALUE */ int LOWEST_PRECEDENCE = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
至此,我们就能理解为什么@Autowired能够通过属性名注入不同的bean了。
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作能带来一定的帮助,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对我们的支持。

